While Lyme disease is the most common tick-borne infection in Delaware, there are other tick-associated diseases to be aware of in case you suffer a tick bite.
This page lists the most common tick-associated infections found in Delaware, with information about which ticks in Delaware can cause which health issues, and with links to the website of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information.
Health care providers may conduct diagnostic testing to determine if you have been infected with a tick-borne pathogen. Alternatively, they may choose to diagnose based on your symptoms and exposure (e.g., taking into consideration the time of year, geographic location, and if you had a known tick bite), without testing.
Most tick-associated illnesses can be easily treated, however, a delay in diagnosis or treatment can lead to more severe illness that is more difficult to treat.
Lyme disease is the most common tick-borne infection in Delaware and in North America. In 2020, there were 346 confirmed cases of Lyme disease in Delaware.
The causative agent is Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria. It is carried by the blacklegged or deer tick (Ixodes scapularis).
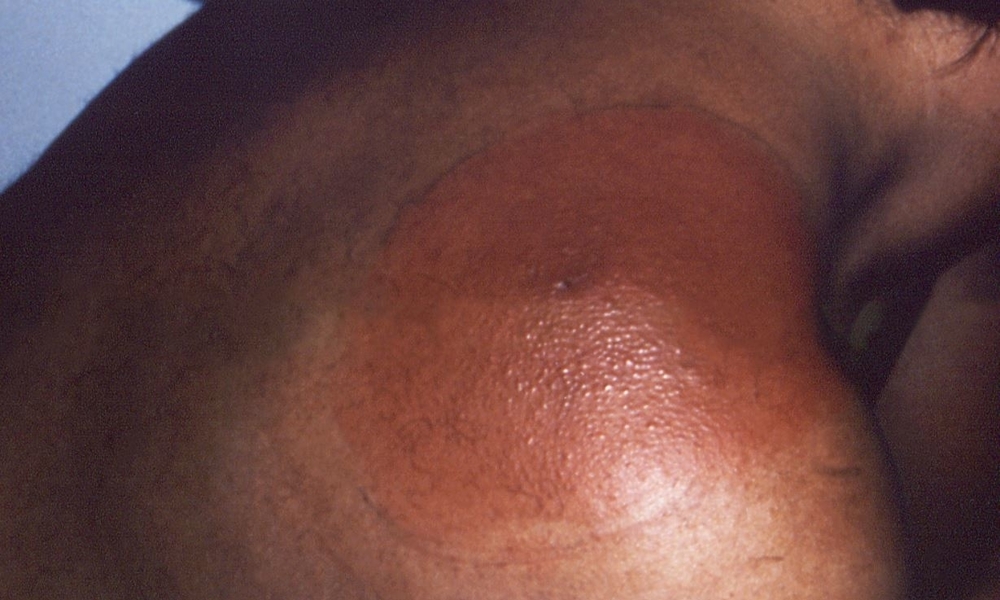
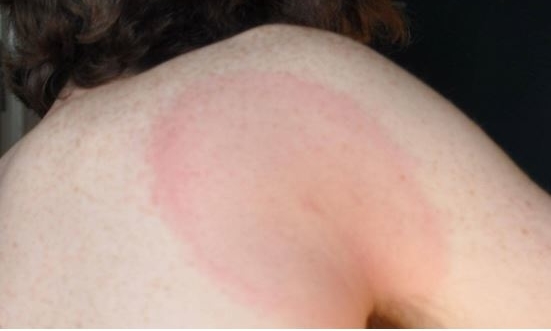
Clinical signs and symptoms may include fever, aches, fatigue, and a distinctive rash (pictured). More serious symptoms can result from delayed or inadequate treatment.
Learn more from the Delaware Division of Public Health.
Ehrlichiosis is caused by infection with bacteria in the genus Ehrlichia.
The main vector of Ehrlichia bacteria in Delaware is the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum).
Clinical signs and symptoms may include fever, aches, gastrointestinal upset, and a rash.
Anaplasmosis is caused by infection with Anaplasma phagocytophilum bacteria.
These bacteria are transmitted by the bite of a blacklegged/deer tick (Ixodes scapularis).
Clinical signs and symptoms may include fever, aches, and gastrointestinal upset.
Babesiosis is caused by infection with Babesia microti. Unlike the other tick-borne pathogens in Delaware, this pathogen is not bacterial, but a protozoan parasite (similar to the causative agent of malaria). In 2020, there were 3 confirmed cases of babesiosis in Delaware.
These parasites are carried by the blacklegged/deer tick, (Ixodes scapularis).
Clinical signs and symptoms may include fever, aches, nausea, and fatigue.
Bacteria in the genus Rickettsia cause Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Tidewater spotted fever, and closely related illnesses. In 2020, there were 20 probable cases of spotted fever rickettsiosis in Delaware.
American dog ticks (Dermacentor variabilis) transmit Rickettsia rickettsii, the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Gulf Coast ticks (Amblyomma maculatum) transmit Rickettsia parkeri, the agent of Tidewater spotted fever.
Clinical signs and symptoms include fever, aches, gastrointestinal upset, and a rash.
Unlike the other diseases on this list, alpha-gal syndrome or mammalian meat allergy is not caused by a pathogen or an infectious agent.
It is a condition that begins with the bite of a lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), which triggers an immune reaction to subsequent ingestion of mammalian meat and related products (e.g., dairy, gelatin).
Not everyone who is bitten by a lone star tick will develop this allergy.
Signs and symptoms of alpha-gal syndrome may include rash, hives, gastrointestinal upset, and dizziness.
Tularemia is caused by infection with Francisella tularensis bacteria. In 2020, there was one confirmed case of tularemia in Delaware.
The main vectors of tularemia in Delaware are the American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis) and the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum).
Clinical signs and symptoms include fever, skin ulcers, and swelling of lymph glands.
Related Topics: dfw, disease, fish and wildlife, Health and Safety, lyme, tick